- What Is Low-Voltage Switchgear?
- Where Is Low-Voltage Switchgear Used?
- Industry Trends & Market Background
- Technical Specifications and Components
- LV vs MV vs HV Switchgear: Key Differences
- How to Choose the Right Low-Voltage Switchgear
- Real-World Benefits of Low-Voltage Switchgear
- Trusted References
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
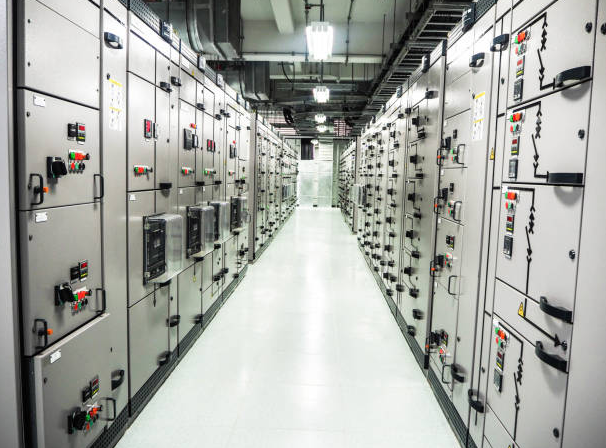

What Is Low-Voltage Switchgear?
Low-voltage switchgear is an assembly of electrical components used to manage power distribution for voltages up to 1,000V AC or 1,500V DC, most commonly 230V/400V systems. It combines circuit breakers, disconnect switches, contactors, relays, meters, and busbars within a protective enclosure.
Its primary purpose is to:
- Safely switch on/off electrical circuits
- Protect systems against overloads, short circuits, and faults
- Ensure continuity of power during maintenance or fault isolation
- Support control and automation functions in modern facilities
Where Is Low-Voltage Switchgear Used?
Low-voltage switchgear is essential across various sectors, including:
- Commercial Buildings – Shopping malls, offices, and hospitals
- Industrial Facilities – Machinery control in manufacturing plants
- Data Centers – Ensures uninterrupted power distribution
- Residential Complexes – Local load protection and metering
- Renewable Energy Systems – Final distribution in solar and wind farms
- Infrastructure Projects – Airports, railways, and utilities
Whether managing lighting circuits or powering motors, low-voltage switchgear ensures secure and reliable operation across end-user systems.
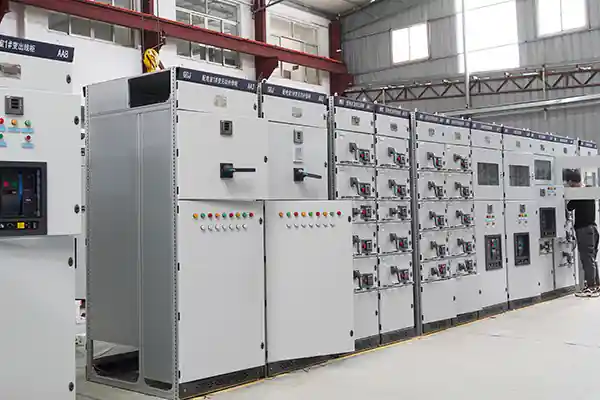

Industry Trends & Market Background
According to IEEMA and MarketsandMarkets, the global low-voltage switchgear market is expected to exceed USD 60 billion by 2030, driven by:
- Smart building adoption
- Grid modernization and decentralization
- Rising demand for energy efficiency
- Urban infrastructure expansion
Innovations such as IoT-enabled switchgear, modular designs, and AI-based fault diagnostics are pushing traditional LV systems into the realm of digital power management.
IEEE standard C37.20.1 and IEC standard 61439-1 govern the design, safety, and testing of low-voltage switchgear globally.
Technical Specifications and Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Circuit Breakers | Overload and short-circuit protection |
| Busbars | Current distribution within panels |
| Contactors | Remote switching of electrical loads |
| Relays | Sensing and fault detection |
| Meters & Indicators | Voltage, current, and power quality monitoring |
| Enclosure (IP rated) | Protection against dust, moisture, and arc faults |
Typical voltage: 230V / 400V / 690V
Typical current range: 100A – 6,300A
Breaking capacity: Up to 100kA
Form: Fixed, withdrawable, or modular
Protection class: IP40 to IP65 (for harsh environments)
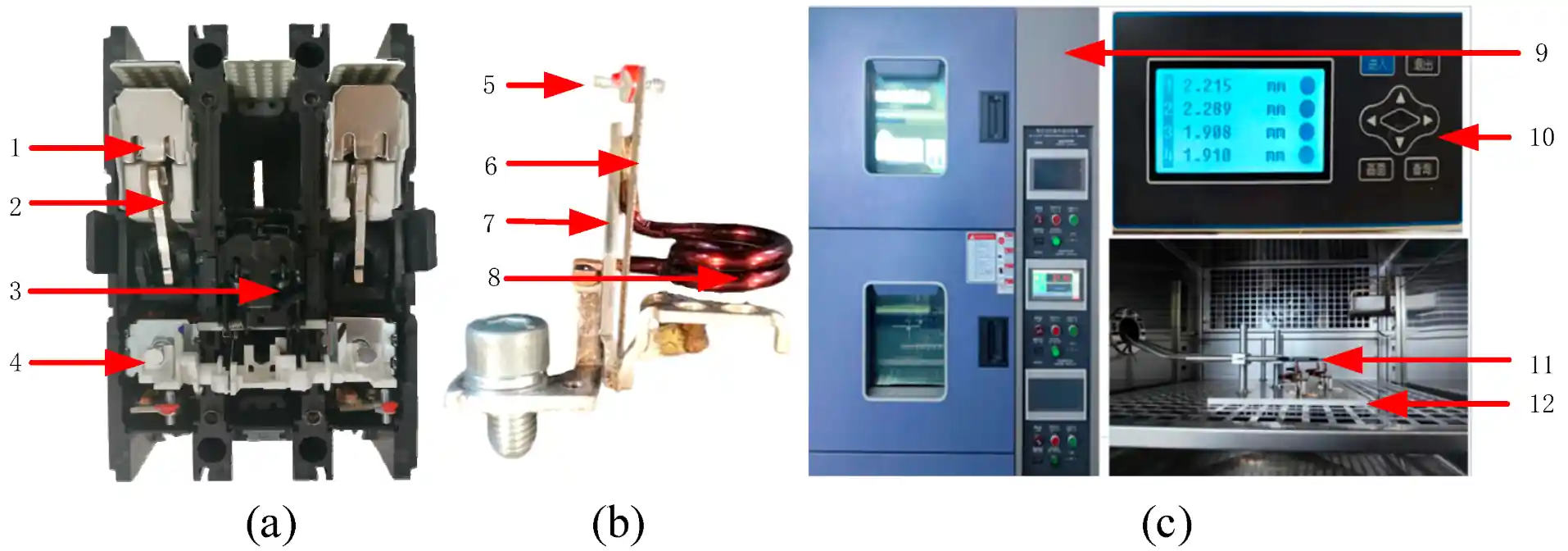
LV vs MV vs HV Switchgear: Key Differences
| Feature | Low Voltage (LV) | Medium Voltage (MV) | High Voltage (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | Up to 1kV | 1kV to 36kV | Above 36kV |
| Typical Use | End-user and load centers | Primary distribution | Transmission & grid interface |
| Switching Devices | MCBs, MCCBs, ACBs | VCBs, LBS, SF₆ CBs | SF₆ CBs, Air/Hybrid CBs |
| Maintenance Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Installation | Indoor panels | Indoor/outdoor metal-clad | Outdoor substations |
How to Choose the Right Low-Voltage Switchgear
Here are some key factors to consider when selecting LV switchgear:
- Load Type and Size: Ensure current rating and short-circuit capacity match load requirements
- Safety Standards Compliance: Look for IEC 61439-1 or UL 1558 compliance
- Flexibility & Modularity: Opt for modular panels for future expansion
- Protection Level: Use higher IP-rated panels for dusty or humid environments
- Control Needs: Include metering, remote control, or SCADA integration for advanced operations
- Manufacturer Reliability: Choose from proven brands like ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Eaton, or trusted regional suppliers like PINEELE
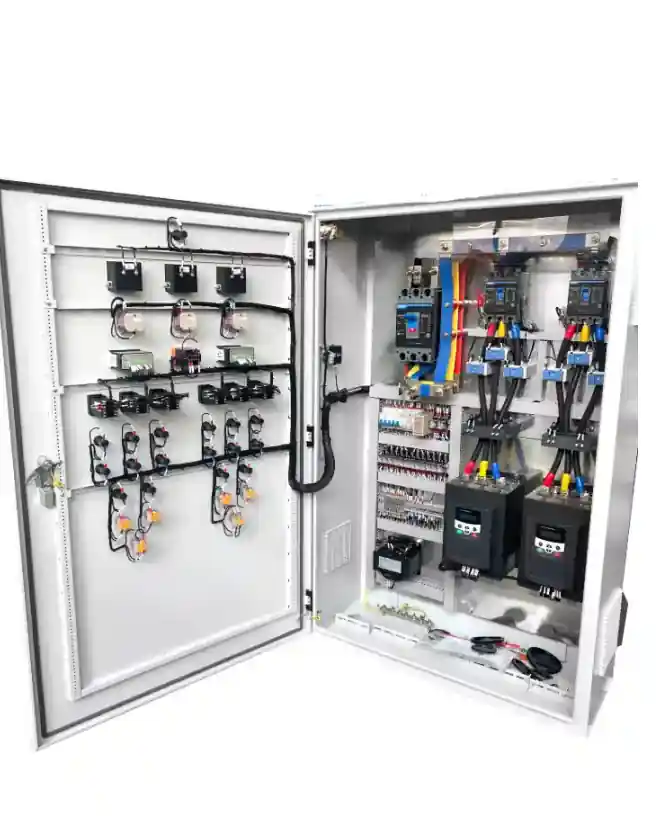

Real-World Benefits of Low-Voltage Switchgear
- Improved Safety: Isolates fault zones and protects personnel
- Reduced Downtime: Enables selective fault clearing and faster maintenance
- Scalable Power Management: Supports future load growth and automation
- Cost Efficiency: Lower capital and operating costs vs higher voltage systems
Trusted References
- IEEE C37.20.1 – Standard for Metal-Enclosed Low-Voltage Switchgear
- Wikipedia: Switchgear
- IEC 61439-1 Standard Overview
- ABB – Low Voltage Switchgear Portfolio
- Schneider Electric – Prisma LV Panels
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
A: Its core functions are to distribute power, protect circuits from faults, and enable safe operation and maintenance of electrical systems under 1,000 volts.
A: Yes, if it has an enclosure with sufficient protection (typically IP54–IP65) and is designed to withstand weather conditions.
A: Modular switchgear offers greater flexibility, easier maintenance, and supports system upgrades—making it a better long-term investment for most users.
Low-voltage switchgear may not operate at the towering voltages seen in transmission systems, but its role is equally vital. From protecting electrical infrastructure to enabling intelligent control in smart buildings, it serves as the backbone of safe and efficient power distribution at the user level.
Whether you’re specifying equipment for a new factory or upgrading your building’s electrical system, understanding the purpose and design of LV switchgear empowers you to make better, safer, and more cost-effective decisions. Always rely on certified manufacturers, comply with global standards, and tailor configurations to your specific needs.
