
Introduction to RMUs
A Ring Main Unit (RMU) is a vital piece of switchgear used in medium-voltage power distribution systems, typically operating at voltages of 11kV to 33kV. It serves as a critical node for ensuring the continuous, safe, and reliable supply of electricity, especially in looped or meshed networks. RMUs combine multiple functions in one compact, sealed unit: switching, isolating, and protecting different sections of a distribution grid.
The Core Purpose of an RMU
The fundamental purpose of an RMU is to:
- Maintain uninterrupted power by allowing isolation of faults without affecting the rest of the network.
- Enable load transfer between feeder lines in a ring distribution system.
- Protect transformers and cable feeders with circuit breakers and fuses.
- Provide remote and manual switching for operational flexibility.
In essence, RMUs are the backbone of resilient, fault-tolerant distribution networks.

Application Fields
RMUs are extensively used in:
- Urban and suburban power distribution
- Industrial parks and factories
- Commercial complexes and high-rise buildings
- Renewable energy grids (solar and wind farms)
- Public infrastructure (hospitals, metros, airports)
They are especially useful where space constraints and high reliability are paramount.
Market Context and Trends
According to Mordor Intelligence and IEEMA reports, the RMU market is growing steadily, driven by:
- The global shift toward smart grids
- Increasing urbanization and electrification
- Emphasis on power reliability and safety
- Rising deployment of renewable energy sources
Major manufacturers like ABB, Schneider Electric, and Eaton are leading innovations in compact, eco-friendly RMU designs.
Technical Parameters (Typical 12kV RMU)
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 12kV |
| Rated Current | 630A |
| Short Circuit Rating | 20-25kA |
| Insulation Type | SF₆ / Solid Dielectric |
| Protection Degree | IP54 / IP65 |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 62271-100 / 200 / 103 |
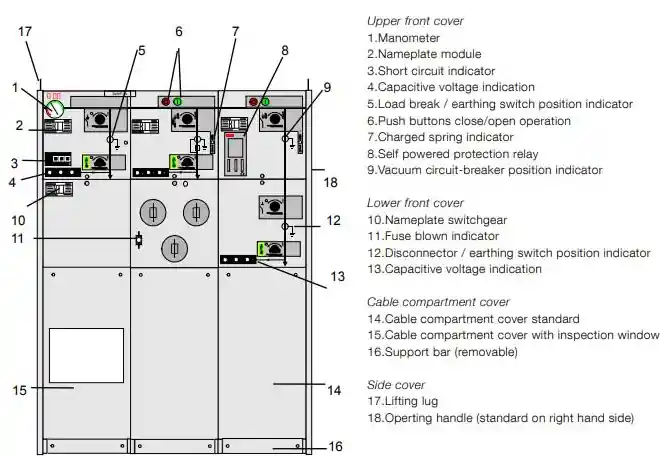
RMU vs Traditional Switchgear
| Feature | Ring Main Unit (RMU) | Traditional Switchgear |
| Size | Compact | Larger footprint |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular servicing |
| Operation | Manual / Motorized / Remote | Mostly manual |
| Safety | High (sealed enclosure) | Moderate |
| Installation Area | Indoor / Outdoor | Mostly indoor |
Buying and Selection Guide
When choosing an RMU, consider:
- Rated voltage and current needs
- Preferred insulation medium (SF₆ gas vs. solid dielectric)
- Configuration type (2-way, 3-way, 4-way)
- Remote monitoring and automation capabilities
- Compliance with IEC and local utility standards
Leading options include models by PINEELE, Siemens, ABB, and Lucy Electric.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A1: RMUs offer redundancy, compactness, and fault isolation, allowing power to reroute during maintenance without affecting end-users.
A2: While SF₆ is effective, many manufacturers now offer solid-insulated alternatives due to environmental concerns.
A3: High-quality RMUs typically offer lifespans of 25–30 years with minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
In modern power networks, the purpose of an RMU goes beyond basic switching. It acts as an intelligent, space-saving solution that enhances grid reliability, operational flexibility, and safety. Whether for industrial, commercial, or renewable energy projects, an RMU remains a cornerstone of efficient medium-voltage distribution systems.
For more insights, refer to standards published by IEEE, Wikipedia, Schneider Electric, and ABB’s technical whitepapers.
