- Core Concept: What Is Switchgear?
- Major Types of Switchgear
- 1. Based on Voltage Level
- 2. Based on Insulation Medium
- 3. Based on Construction and Mounting
- Application Fields
- Market Trends and Innovations
- Technical Parameters Overview
- Differences Between Main Switchgear Types
- Buying Tips and Selection Guidelines
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
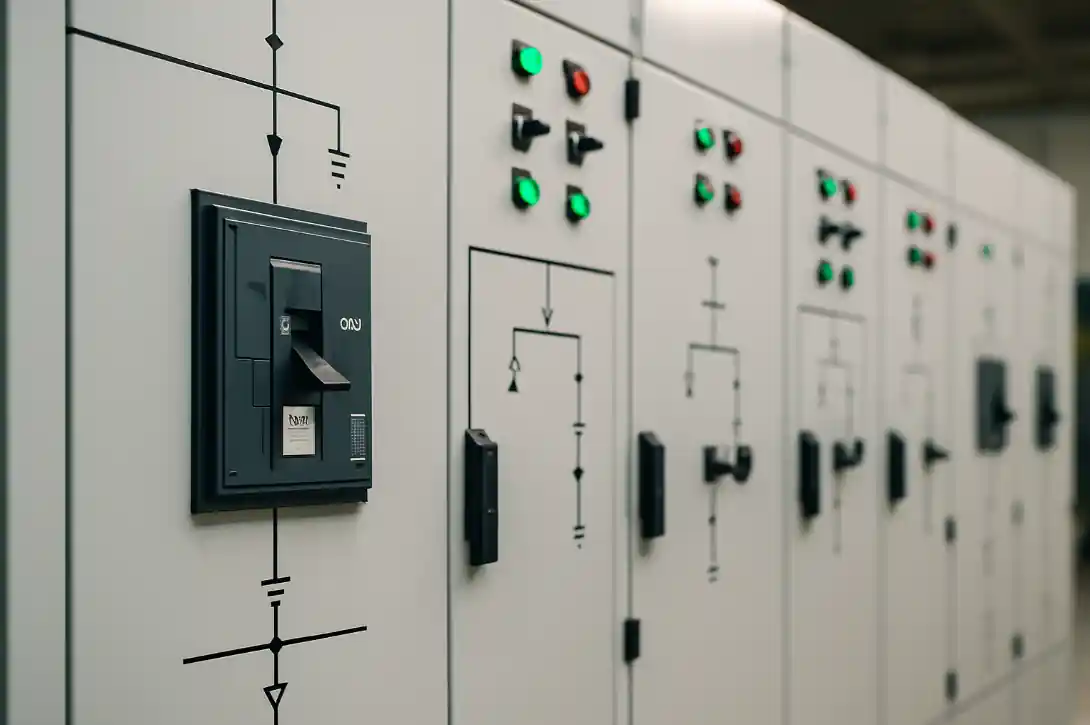

Core Concept: What Is Switchgear?
Switchgear refers to the combination of electrical disconnect switches, fuses, and circuit breakers used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. The primary function of switchgear is to de-energize equipment for maintenance and to clear faults downstream.
According to Wikipedia, switchgear is critical to both the reliability and safety of the electrical supply.
Major Types of Switchgear
1. Based on Voltage Level
- Low Voltage (LV) Switchgear: Up to 1kV; common in residential, commercial, and small industrial applications.
- Medium Voltage (MV) Switchgear: 1kV to 36kV; used in larger industrial plants, substations, and renewable energy installations.
- High Voltage (HV) Switchgear: Above 36kV; critical for transmission networks and large utility systems.

2. Based on Insulation Medium
- Air Insulated Switchgear (AIS): Economical, widely used in outdoor installations.
- Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS): Compact, filled with SF6 gas, excellent for space-constrained and harsh environments.
- Vacuum Switchgear: Utilized for medium voltage systems where vacuum interrupters offer efficient arc quenching.
- Oil Insulated Switchgear: Historically common, now less favored due to maintenance and environmental concerns.
3. Based on Construction and Mounting
- Metal-Clad Switchgear: All components are enclosed in grounded metal structures; enhanced safety.
- Metal-Enclosed Switchgear: Components are enclosed but not necessarily segregated by function.
- Pad-Mounted Switchgear: Ground-level enclosures commonly used in urban distribution.
Application Fields
- Utility Power Grids: Ensuring continuous energy supply and fault management.
- Industrial Facilities: Protecting heavy machinery, motors, and process systems.
- Renewable Energy Plants: Managing solar and wind energy integration into the grid.
- Commercial Buildings: Electrical distribution in malls, hospitals, and data centers.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Metro systems, airports, and railways.
IEEE research emphasizes the growing use of gas-insulated and smart switchgear systems in urban infrastructure.
Market Trends and Innovations
- Smart Switchgear: Integration with IoT and SCADA systems for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: GIS using alternative gases to replace SF6, reducing environmental impact.
- Modular Configurations: Manufacturers like ABB, Schneider Electric, and Siemens offer plug-and-play modular switchgear for faster deployment.
- Digital Twin Technology: Virtual modeling for better maintenance planning and fault prediction.
According to IEEMA reports, demand for smart and green switchgear is accelerating globally.
Technical Parameters Overview
| Parameter | Low Voltage Switchgear | Medium Voltage Switchgear | High Voltage Switchgear |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | Up to 1kV | 1kV – 36kV | Above 36kV |
| Rated Current | Up to 6000A | Up to 4000A | Up to 4000A or more |
| Breaking Capacity | Moderate | High | Very high |
| Protection Level | IP30-IP65 | IP40-IP67 | IP54-IP68 |
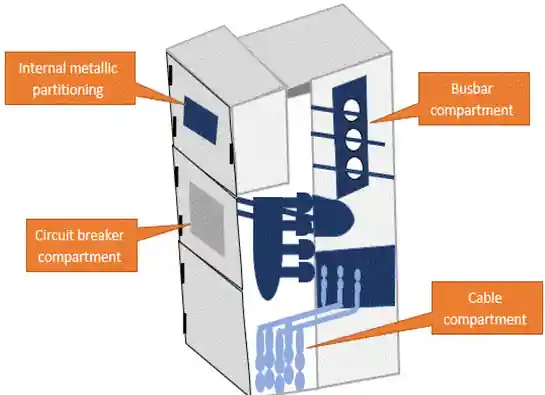
Differences Between Main Switchgear Types
| Feature | AIS | GIS | Vacuum Switchgear |
| Space Requirements | High | Low | Moderate |
| Maintenance Needs | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Environmental Tolerance | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Lifetime | 20-30 years | 30-40 years | 25-30 years |
Choosing the right type depends heavily on site conditions, budget, and long-term maintenance planning.
Buying Tips and Selection Guidelines
- Define Application Needs: Voltage level, load type, and fault levels.
- Space Constraints: Choose GIS if space is limited.
- Environmental Factors: For humid or corrosive environments, GIS or vacuum types are preferable.
- Scalability: Select modular systems if future expansions are likely.
- Supplier Reputation: Prefer products from certified manufacturers such as ABB, Schneider Electric, Eaton, or Siemens.
Selecting the correct switchgear ensures safety, operational efficiency, and lower lifecycle costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A1: Well-maintained switchgear typically lasts 20–40 years depending on the type and operating environment.
A2: GIS is compact, requires minimal maintenance, and provides high protection against environmental factors, making it ideal for densely populated areas.
A3: Absolutely. Low voltage switchgear is commonly used to manage distributed generation assets like rooftop solar PV systems.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of switchgear is vital for designing resilient, efficient, and safe electrical systems. As energy systems become smarter and greener, selecting the right switchgear will be even more critical to achieving operational excellence and sustainability.
