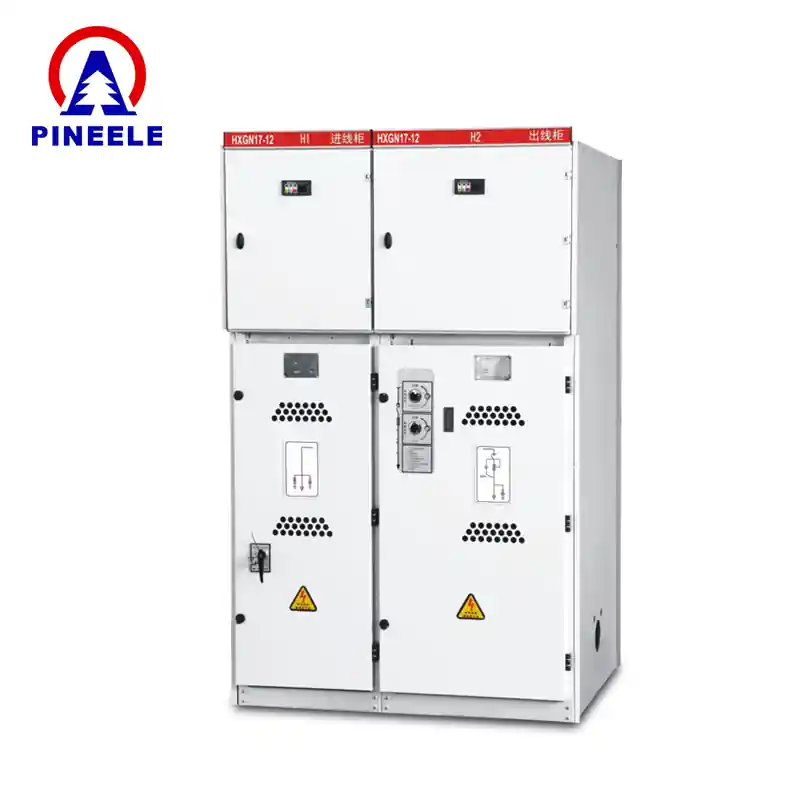

Introduction to RMUs
ARing Main Unit (RMU)is a vital piece of switchgear used in medium-voltage power distribution systems, typically operating at voltages of 11kV to 33kV. It serves as a critical node forensuring the continuous, safe, and reliable supply of electricity, especially in looped or meshed networks. RMUs combine multiple functions in one compact, sealed unit:switching, isolating, and protectingdifferent sections of a distribution grid.
The Core Purpose of an RMU
The fundamental purpose of an RMU is to:
- Maintain uninterrupted powerby allowing isolation of faults without affecting the rest of the network.
- Enableload transferbetween feeder lines in a ring distribution system.
- Protect transformers and cable feederswith circuit breakers and fuses.
- Provideremote and manual switchingfor operational flexibility.
In essence, RMUs are the backbone of resilient, fault-tolerant distribution networks.
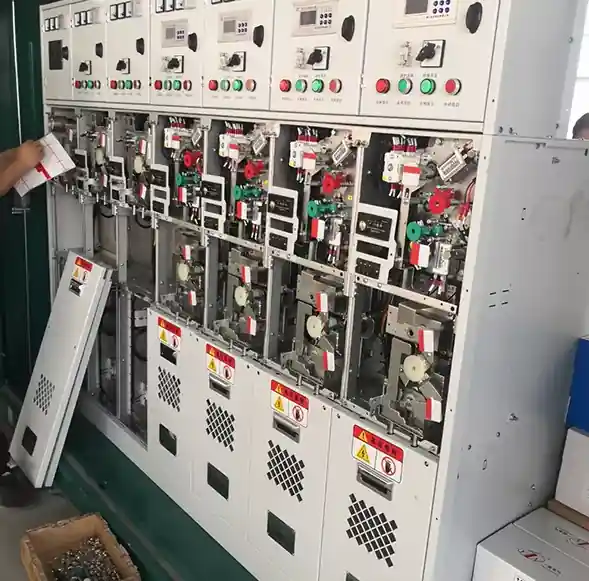

Application Fields
RMUs are extensively used in:
- Urban and suburban power distribution
- Industrial parks and factories
- Commercial complexes and high-rise buildings
- Renewable energy grids(solar and wind farms)
- Public infrastructure(hospitals, metros, airports)
They are especially useful wherespace constraintsandhigh reliabilityare paramount.
Market Context and Trends
According toMordor IntelligenceandIEEMAreports, the RMU market is growing steadily, driven by:
- The global shift towardsmart grids
- Increasingurbanization and electrification
- Emphasis onpower reliability and safety
- Rising deployment ofrenewable energy sources
Major manufacturers likeABB,Schneider Electric, andEatonare leading innovations in compact, eco-friendly RMU designs.
Technical Parameters (Typical 12kV RMU)
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 12kV |
| Rated Current | 630A |
| Short Circuit Rating | 20-25kA |
| Insulation Type | SF₆ / Solid Dielectric |
| Protection Degree | IP54 / IP65 |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 62271-100 / 200 / 103 |
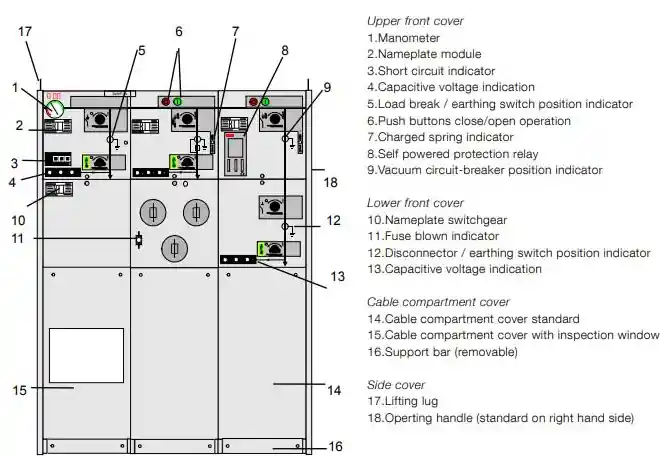
RMU vs Traditional Switchgear
| Feature | Ring Main Unit (RMU) | Traditional Switchgear |
| Size | Compact | Larger footprint |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular servicing |
| Operation | Manual / Motorized / Remote | Mostly manual |
| Safety | High (sealed enclosure) | Moderate |
| Installation Area | Indoor / Outdoor | Mostly indoor |
Buying and Selection Guide
When choosing an RMU, consider:
- Rated voltage and currentneeds
- Preferredinsulation medium(SF₆ gas vs. solid dielectric)
- Configuration type(2-way, 3-way, 4-way)
- Remote monitoring and automationcapabilities
- Compliance withIEC and local utility standards
Leading options include models byPINEELE,Siemens,ABB, andLucy Electric.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A1:RMUs offerredundancy, compactness, and fault isolation, allowing power to reroute during maintenance without affecting end-users.
A2:WhileSF₆ is effective, many manufacturers now offersolid-insulated alternativesdue to environmental concerns.
A3:High-quality RMUs typically offerlifespans of 25–30 yearswith minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
In modern power networks, thepurpose of an RMUgoes beyond basic switching. It acts as an intelligent, space-saving solution that enhancesgrid reliability, operational flexibility, and safety. Whether for industrial, commercial, or renewable energy projects, an RMU remains a cornerstone of efficient medium-voltage distribution systems.
For more insights, refer to standards published byIEEE,Wikipedia,Schneider Electric, andABB’s technical whitepapers.
